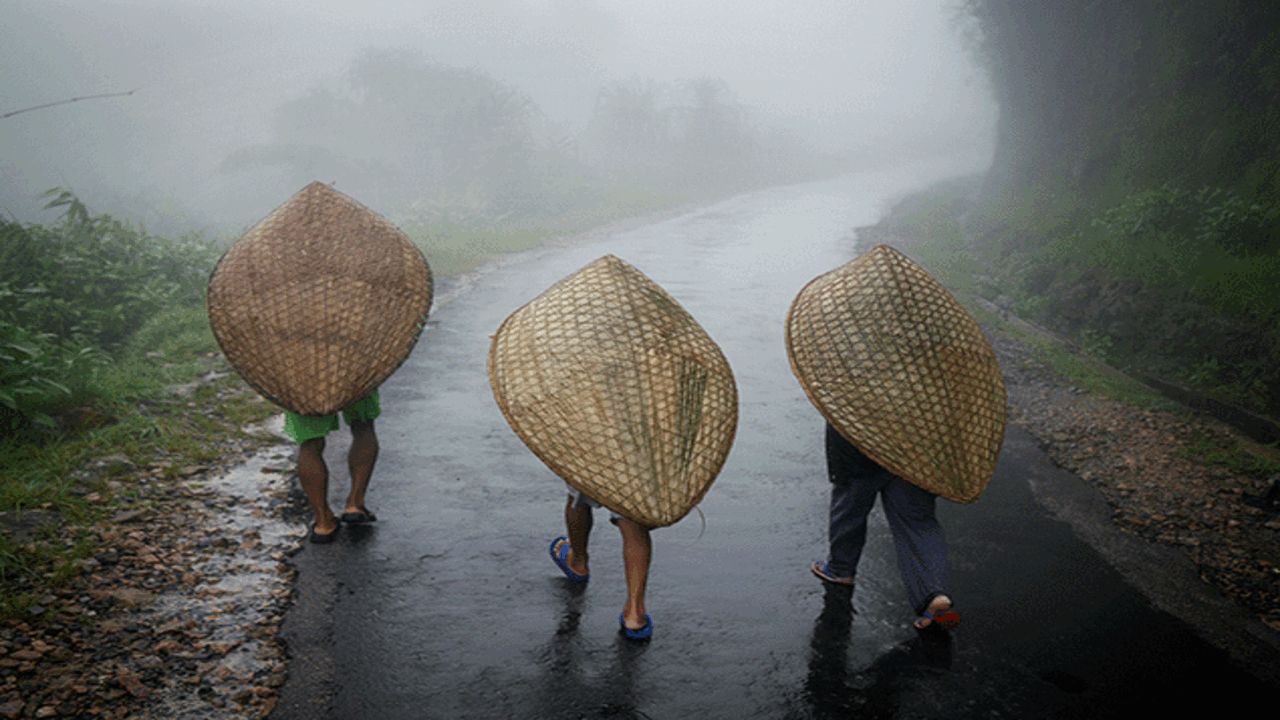
Mawsynram in the Indian state of Meghalaya, famous for being the wettest place in the world for so long, has recently been observing a disturbing decrease in rainfall levels, which was attributed to the rising levels of air pollution, according to new studies. Researchers say that if air pollution levels are not managed soon, there would be serious threats to the climate in that region.
According to a study published in the Journal of the Indian Society of Remote Sensing, Mawsynram’s average annual rainfall was found to decline substantially during the past decade. It was found that the average rainfall decreased from 10,235 mm in 2014 to 8,838.2 mm in 2023, a decrease of about 13.6 percent. This is a remarkable finding because Mawsynram is well-known worldwide for its highest average annual rain.
The research work conducted by Mamta Devi and a team of researchers to interpret the satellite and atmospheric data in terms of the evolving trends in the rainfall pattern revealed a close linkage between the reduction in the amount of rains and the rise in the concentration of aerosols in the atmosphere; the latter being a collection of tiny particles suspended in the atmosphere due to various sources of pollution like car emissions and other types of burning processes.
The researchers were able to detect the aerosol optical depth, an indicator of the amount of particulate air pollution, by using satellite observations. The results showed that an overall increase of 15 per cent in the aerosol optical depth was recorded in the Mawsynram area between 2014 and 2023, with an annual increase of 0.007 units. Even more alarming was the 9 per cent rise in the fine-mode aerosols, particulate matter in the air, which is small enough to stay suspended in the air for an extended period of time, with significant effects on formation of clouds.
According to the study, when the levels of such fine aerosol particles are high, they interfere with the natural mechanism by which clouds produce rain. This is the case because, in the natural mechanism, rain formation in clouds is achieved through the collision of water droplets in clouds, which eventually become heavy enough to fall into rain.
On the other hand, when there are a lot of aerosols in the atmosphere, they form a number of small droplets in clouds that fail to combine in a way that can form rain, thus the low levels of rain in Mawsynram.
Furthermore, besides impacting cloud dynamics, aerosols were also discovered to impact the energy balance in the region. It was found that there was a noticeable increase in the aerosol radiative forcing. During the winter season, the aerosol radiative forcing increased from 11.81 to 18.26 watts/sq. meter, while in the pre-monsoon season, the increase in aerosol radiative forcing was found to be from 15.47 to 21.66 watts/sq. meter.
Therefore, more warming of the atmosphere occurs with the consequent impact of disturbing the patterns of weather and rain.Aerosol pollution was found to be highest during the winter and pre-monsoon periods when atmospheric conditions facilitate the holding of pollutants close to the ground. Though pollution levels during monsoon conditions were relatively low, they still existed in sufficient proportions to affect cloud formation.
Even during post-monsoon periods, atmospheric pollution was found to influence atmospheric conditions, thereby showing that pollution effects remain even during different periods of a year.However, researchers have now clarified that these results emphasize the complex interactions that exist or can exist between air pollution and regional climatic elements. Contributing authors Sumit Kumar Mishra, Kartika Pandey, Supreet Kaur, Anikender Kumar, Vijay Kumar Soni, Amarendra Singh, and Atul Kumar Srivastava specifically added that aerosol-cloud interactions need to be better explored; otherwise, there can be limitations in improving climatic or rainforests-related models in north or northeast India.
Experts assert that reduced rainfall in Mawsynram is a warning signal with implications beyond mere reduced rainfall. Decreased precipitation will have repercussions in agriculture, water availability, and sensitive ecosystems that rely heavily on precipitation. The scientists demanded that measures should be taken immediately to counter air pollution and ensure application of scientific knowledge in regional planning initiatives.
While Mawsynram’s claim to be the world’s wettest regions appears to be called into question, it is a reminder that air pollution needs to be considered not simply as a determinant of human health but also as a factor capable of recalculating climate patterns.